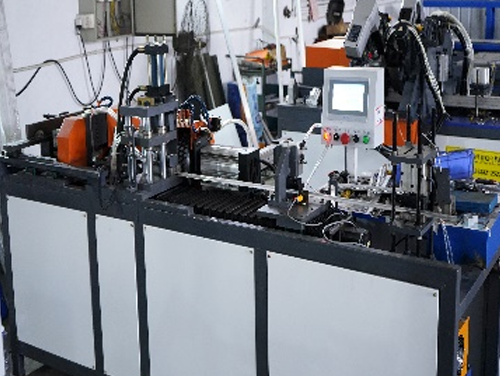
Luggage Hinge Machine Productivity Metrics: A Technical Perspective
Industry Background and Market Demand
The luggage manufacturing industry relies heavily on precision components, with hinges being a critical element in ensuring durability and functionality. As consumer expectations for lightweight yet robust luggage rise, manufacturers must optimize hinge production to meet quality and efficiency demands.
Luggage hinge machines are specialized equipment designed to produce hinges with high repeatability and minimal defects. The market for these machines is driven by the growing travel industry, increasing demand for premium luggage, and the need for automation in manufacturing. Companies investing in advanced hinge production systems seek measurable productivity gains to justify capital expenditures.
Core Concepts and Key Technologies
Productivity metrics for luggage hinge machines evaluate output efficiency, precision, and operational reliability. Key performance indicators (KPIs) include:
- Cycle Time: The time taken to complete one hinge production cycle.
- Defect Rate: The percentage of hinges failing quality inspections.
- Uptime/Downtime Ratio: Machine availability versus maintenance or stoppage periods.
- Material Utilization: Waste reduction in metal or polymer processing.
Modern hinge machines integrate servo-driven mechanisms, CNC controls, and real-time monitoring systems to enhance these metrics. Advanced sensors detect misalignments or material inconsistencies, reducing scrap rates.
Product Structure, Performance, and Manufacturing Process
A typical luggage hinge machine consists of:
- Feeding System: Automated material input (e.g., steel strips or polymer sheets).
- Stamping/Punching Unit: Forms hinge components with high-pressure dies.
- Bending/Assembly Module: Shapes and joins hinge parts.
- Quality Control Station: Vision systems or laser measurement for dimensional accuracy.
Performance depends on:
- Tooling Precision: Hardened steel dies ensure longevity and consistency.
- Actuation Speed: Servo motors enable adjustable speeds for different materials.
- Lubrication Systems: Reduce friction and wear in high-cycle operations.
Manufacturing processes vary based on hinge type (e.g., piano hinges, snap hinges). Metal hinges often undergo stamping, bending, and surface treatment (e.g., plating), while polymer hinges may use injection molding.
Critical Factors Affecting Quality and Performance
Several variables influence hinge machine productivity:
1. Material Properties: Variations in metal hardness or polymer viscosity affect forming consistency.
2. Tool Wear: Progressive die degradation increases defect rates; scheduled maintenance is essential.
3. Machine Calibration: Misaligned punches or dies lead to dimensional inaccuracies.
4. Operator Skill: Proper setup and troubleshooting minimize unplanned downtime.
Supplier Selection and Supply Chain Considerations
When sourcing hinge machines, manufacturers evaluate:
- Technical Support: Availability of maintenance training and spare parts.
- Customization Capabilities: Adaptability to different hinge designs.
- Compliance Standards: ISO certifications and adherence to safety regulations.
- Lead Times: Equipment delivery and installation schedules.
Reliable suppliers offer modular designs, allowing future upgrades (e.g., IoT integration for predictive maintenance).
Common Challenges and Industry Pain Points
Key issues in hinge production include:
- High Initial Costs: Advanced machines require significant investment.
- Material Waste: Inefficient cutting or stamping increases scrap.
- Downtime: Unplanned stoppages disrupt production schedules.
- Compatibility Issues: Retrofitting older machines for new hinge designs can be costly.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Luggage hinge machines serve:
- OEMs: Large-scale manufacturers producing branded luggage.
- Component Suppliers: Specialized firms supplying hinges to multiple brands.
- Aftermarket Providers: Replacement hinge production for repairs.
A case study involves a European luggage manufacturer that reduced defect rates by 30% after upgrading to a servo-controlled hinge machine with automated QC.
Current Trends and Future Developments
Emerging advancements include:
- Smart Manufacturing: IoT-enabled machines for real-time performance tracking.
- Sustainable Materials: Machines adapted for biodegradable polymers or recycled metals.
- AI-Driven Optimization: Predictive analytics for tool wear and maintenance scheduling.
Future hinge machines may incorporate collaborative robotics (cobots) for flexible, small-batch production.
FAQ
Q: How can manufacturers reduce cycle times without compromising quality?
A: Optimizing servo-motion profiles, minimizing non-productive movements, and using high-speed tooling can improve cycle times while maintaining precision.
Q: What are the most common causes of hinge defects?
A: Misaligned dies, worn tooling, and inconsistent material feed are primary contributors.
Q: Is retrofitting older hinge machines feasible?
A: Yes, but cost-benefit analysis is necessary. Upgrading controls or adding sensors may be more economical than full replacement.
Conclusion
Luggage hinge machine productivity metrics are vital for manufacturers aiming to balance efficiency, quality, and cost. By leveraging advanced technologies and rigorous process controls, companies can enhance output while meeting evolving market demands. Future innovations will further streamline production, making hinge manufacturing more adaptive and sustainable.
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
Comment
(0)